XBRL is a mandatory requirement for nearly all corporate firms to ensure compliance with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. Being a widely adopted format in the corporate world, XBRL provides an encrypted method for sharing crucial financial information with the government using specialized software. In this blog post, we delve into the XBRL filing process and learn about the important due dates associated with the MCA, providing valuable insights for businesses. In this blog post, we will explore the process of filing XBRL and provide information on the important due dates associated with MCA.
We have compiled a calendar that includes all the Important Statutory Due Dates for Public Limited Companies and Private Limited Companies. There are several deadlines on this calendar, including XBRL Annual Return Due Dates, Event-Based Due Dates, AOC-4 (XBRL) due date, Form CRA-4 due date and more.
Introduction About XBRL?
XBRL is a language used for electronically exchanging business and financial records that brings a transformative impact on business reporting worldwide. It offers significant advantages in terms of preparing, analyzing, and communicating business reports. It brings cost savings, increased efficiency, and enhanced precision and dependability for all stakeholders involved in the provision or utilization of financial records. XBRL can be referred to as an eXtensible Business Reporting Language. It is already being implemented in several countries and is experiencing rapid growth on a global scale.
Which Companies Need to Submit Financial Statements to the Registrar using XBRL Taxonomy?
The categories listed below are obligated to file their financial statements and related documents under section 137 of the Act with the Registrar in e-form AOC-4 XBRL, as specified in Annexure-I:
(i) Companies listed on Indian stock exchanges and their Indian subsidiaries.
(ii) Companies with a paid-up capital of five core rupees or more.
(iii) Companies with a turnover of one hundred crore rupees or more.
(iv) All companies that are required to prepare their financial statements under the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015.
It is important to note that companies making their financial statements under the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 should file their statements through the Taxonomy furnished in Annexure-II, while companies making their financial statements under Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015, should submit their statements through the Taxonomy furnished in Annexure-II A.
Provided that the Non-banking financial companies, Housing finance companies, and Companies involved in the business of the banking and insurance sector are privileged from the furnishing of the financial statements.
Besides section 137, the companies and firms who have furnished their financial statements in XBRL shall carry on furnishing their financial statements along with the other credentials in XBRL only, however, they might cease to fall under the purview of this section.
Key Components of XBRL Filing:
Before delving into the due dates, let’s understand the key components of XBRL filing:
- Financial Statements: Companies are required to convert their financial statements into XBRL format. This includes the balance sheet, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and other relevant documents.
- Taxonomies: XBRL taxonomies are predefined frameworks that define the elements and relationships in financial statements. These taxonomies serve as a standardized dictionary for reporting financial information.
- Instance Documents: The prepared financial statements in XBRL format are encapsulated in instance documents, which are then submitted to the MCA.
Read Also: ROC (MCA) MGT 7 Annual Return Due Date
How does XBRL (EXTENSIBLE BUSINESS REPORTING LANGUAGE) run?
XBRL exhibits the data readable through the guidance provided from two documents
- Taxonomy and
- Instance document
Taxonomy is based on the objectives and their relationships based on the needs of the law. Using the taxonomy prescribed through the regulators, companies can navigate the reports and create a valid XBRL quicker document. The steps of mapping consist of matching the concepts as reported through the firms to the identical element in the taxonomy. Moreover, to assign an XBRL tag through the taxonomy, details such as the measurement unit, period of data, scale of reporting, etc., are required to be included in the instance document.
The Credentials Needed for XBRL for MCA
Below are the mentioned documents required to furnish inside the XBRL format:
- Balance Sheet
- Profit and Loss Statement
- Cash Flow Statement
- Schedules associated with Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Statement
- Notes to Accounts
- Audit and Annual Report
- Board Report along with all annexures
- Consolidated Financial Statements (If any)

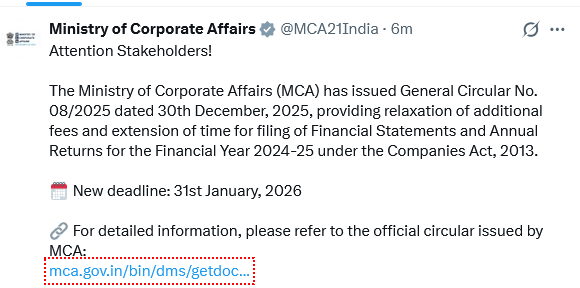
XBRL Filing Due Dates for FY 2024-25
| Name of E-form | Purpose of E-form | Due date of Filing | Due date for FY 2024-25 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form AOC-4 (XBRL) | Filing of Annual Accounts in XBRL mode | 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM | (If AGM held on 30 September, 2025) |
| Form AOC-4 (XBRL) for IND AS based Financial Statement | Filing of Annual Accounts based on Indian Accounting Standard in XBRL mode | 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM | (If AGM held on 30 September, 2025) |
| Form CRA-4 | Filing of Cost Audit Report | 31st December 2025 (Revised) | 30 days from the receipt of Cost Audit Report |
| Form AOC-4 (NBFC) IND and Form AOC-4 CFS (NBFC) IND | Submission of Annual Accounts in Accordance with Indian Accounting Standards for Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFC) | 31st January 2026 (Revised) | 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM |
Latest Update:
- General Circular No. 08/2025 pertains to MGT-7, MGT-7A, AOC-4, AOC-4 CFS, AOC-4 NBFC (Ind AS), AOC-4 CFS NBFC (Ind AS), and AOC-4 (XBRL). Please refer to the Circular for details. Read Circular
- General Circular No. 06/2025 pertains to MGT-7, MGT-7A, AOC-4, AOC-4 CFS, AOC-4 NBFC (Ind AS), AOC-4 CFS NBFC (Ind AS), and AOC-4 (XBRL). Please refer to the Circular for details. Read Circular
- General Circular No. 07/2025 for MCA form CRA-4 pertains to the Cost Audit Report in XBRL format. Read Circular
The Additional Late Fee Penalty:
NOTE: The additional Fee for E-form AOC-4 (XBRL and Non-XBRL) and E-form MGT-7 after the due date is INR 100 per day, effective from 1st July 2018.
In addition to the above, the following table of additional fees shall be applicable for delays in filing of belated annual returns or balance sheet/financial statement under the Companies Act, 1956 or the Companies Act, 2013 up to 30/06/2018:
For Other Documents, Files & Forms Etc
| Period of Delays | Fees |
|---|---|
| Up to 30 days | 2 times of normal fees |
| More than 30 days and up to 60 days | 4 times of normal fees |
| More than 60 days and up to 90 days | 6 times of normal fees |
| More than 90 days and up to 180 days | 10 times of normal fees |
| More than 180 days and up to 270 days | 12 times of normal fees |